概述
K邻子句khop().src().depth()查询从一个点经过最短K步(K条边)能到达的邻居点,即该起点的K步邻居(简称K邻)。
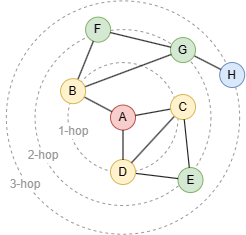
K邻是图论基本概念之一。上图中,点B、C、D是点A的1步邻居,点E、F、G是点A的2步邻居,点H是点A的3步邻居。
K值是唯一的,取决于两点间最短路径的长度。例如,虽然点A、C间存在多条路径(A-C、A-D-C、A-D-E-C),但最短距离是1,因此点C是点A的1步邻居。查询点A的其他步K邻时,不应出现点C。
K邻查询结果应该去重。例如,点A、E间存在两条长度为2的最短路径,但查询点A的2步邻居时,点E只应出现一次。
嬴图使用BFS(广度优先)的方式查找最短路径,进而得到K邻。K邻查询是经过改良大幅提高性能的图近邻查询,在查询节点的邻居节点时,建议使用K邻而非其他等价的路径查询方法。
语法
- 子句别名:NODE类型
- 方法:
方法 |
参数类型 |
参数规范 |
必须 |
描述 | 别名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
src() |
Filter | / | 是 | 起点需满足的条件,只能指定一个起点 | NODE |
depth() |
Range | / | 是 | 搜索深度(N≥1):depth(N):N步depth(:N):1~N步depth(M:N):M~N步(M≥0)当设置为范围时,子句按照由近到远的顺序返回K邻 |
N/A |
node_filter() |
Filter | / | 否 | 查询经过的路径中所有点(除起点外)需满足的条件 | N/A |
edge_filter() |
Filter | / | 否 | 查询经过的路径中所有边需满足的条件 | N/A |
direction() |
String | left,right |
否 | 查询经过的路径中所有边的方向 | N/A |
limit() |
Integer | ≥-1 | 否 | 每个子查询返回的结果数,-1表示返回所有 |
N/A |
使用
node_filter()或edge_filter()排除一部分点或边后,图结构会发生改变,从而影响查询结果。详见过滤点和过滤边示例。
示例
示例图集
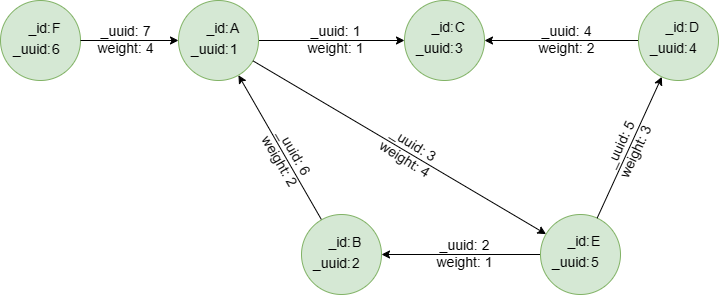
在一个空图集中逐行运行以下语句创建示例图集:
create().edge_property(@default, "weight", int32)
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A", _uuid:1}, {_id:"B", _uuid:2}, {_id:"C", _uuid:3}, {_id:"D", _uuid:4}, {_id:"E", _uuid:5}, {_id:"F", _uuid:6}])
insert().into(@default).edges([{_uuid:1, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:3, weight:1}, {_uuid:2, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:2 , weight:1}, {_uuid:3, _from_uuid:1, _to_uuid:5 , weight:4}, {_uuid:4, _from_uuid:4, _to_uuid:3 , weight:2}, {_uuid:5, _from_uuid:5, _to_uuid:4 , weight:3}, {_uuid:6, _from_uuid:2, _to_uuid:1 , weight:2}, {_uuid:7, _from_uuid:6, _to_uuid:1 , weight:4}])
设置查询深度
查找点D的3步邻居。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| F | 6 |
查找点D的1~3步邻居。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(:3) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| F | 6 |
| B | 2 |
| A | 1 |
| C | 3 |
| E | 5 |
同时返回起点
查找点D的1~2步邻居,并返回点D自身。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(0:2) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| B | 2 |
| A | 1 |
| C | 3 |
| E | 5 |
| D | 4 |
过滤点
要求不经过点E,查找点D的3步邻居。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3).node_filter({_id != "E"}) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| F | 6 |
| B | 2 |
排除点E(及其邻边)后,点B才成为点D的3步邻居。
过滤边
要求不经过5号边,查找点D的3步邻居。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(3).edge_filter({_uuid != 5}) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| E | 5 |
| F | 6 |
| B | 2 |
排除5号边后,点E和B才成为点D的3步邻居。
规定边方向
查找点D的1~2步邻居,要求经过的所有边方向为右。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(:2).direction(right) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| C | 3 |
src()调用别名
查找点D和点F的1步邻居。
find().nodes({_id in ["D", "F"]}) as start
khop().src(start).depth(1).direction(right) as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
结果:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| D | C |
| F | A |
使用limit()
查找3个点D的1~3步邻居。
khop().src({_id == "D"}).depth(:3).limit(3) as n
return n{*}
结果:
| _id | _uuid |
|---|---|
| A | 1 |
| C | 3 |
| E | 5 |
K邻子句按照由近及远的顺序返回起点的K邻,首先返回1步邻居,其次是2步邻居、3步邻居。
使用OPTIONAL
查找点A和D的2步邻居,要求经过的所有边方向为右。无结果时返回null。
find().nodes({_id in ["A", "D"]}) as start
optional khop().src(start).depth(2).direction(right) as n
return table(start._id, n._id)
结果:
| start._id | n._id |
|---|---|
| A | D |
| A | B |
| D | null |
