概述
传导率(Conductance)是用于评估图中社区或聚类质量的指标。研究表明,基于传导率的评分函数最能反映社区的真实结构。
- J. Yang, J. Leskovec, Defining and Evaluating Network Communities based on Ground-truth (2012)
基本概念
传导率
直观地说,好的社区应当在内部紧密连接,但与图的其他部分连接较弱。
对于社区C和图中其他部分C',C的传导率定义为切割大小(C和C'之间的边数)与C和C'之间的最小体积(即其中节点度数之和)的比值:
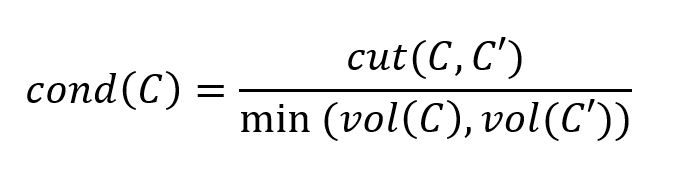
如下例所示,社区C通过3条边与图中其他部分连接,即cut(C, C') = 3。C的传导率为cond(C) = 3/min(19, 17) = 3/17 = 0.176471。
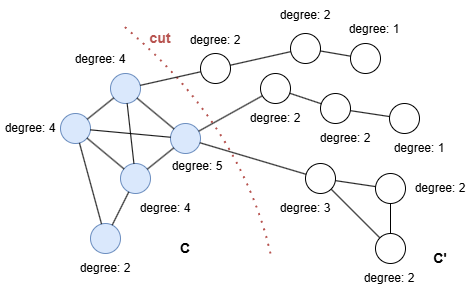
如果调整分割,让社区C多包含一个点,则C的传导率变为cond(C) = 3/min(21, 15) = 3/15 = 0.2。
社区识别中,传导率较小更为理想,这样可以识别内部紧密连接且与外部连接较少的社区。相反,传导率较大,意味着社区内部连接松散,与外部连接较多,表明社区不是紧密连接的。
示例图
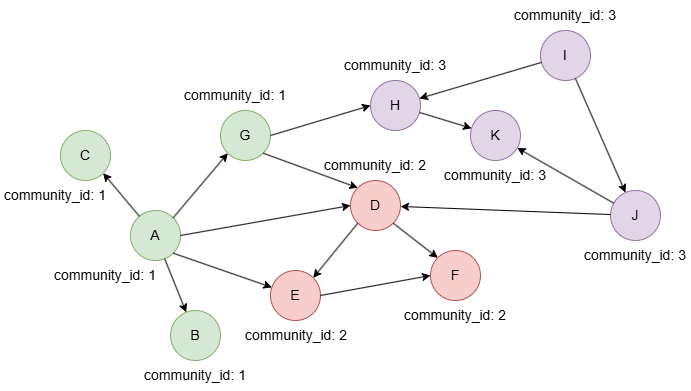
在一个空图中运行以下语句定义图结构并插入数据:
ALTER NODE default ADD PROPERTY {
community_id uint32
};
INSERT (A:default {_id: "A", community_id: 1}),
(B:default {_id: "B", community_id: 1}),
(C:default {_id: "C", community_id: 1}),
(D:default {_id: "D", community_id: 2}),
(E:default {_id: "E", community_id: 2}),
(F:default {_id: "F", community_id: 2}),
(G:default {_id: "G", community_id: 1}),
(H:default {_id: "H", community_id: 3}),
(I:default {_id: "I", community_id: 3}),
(J:default {_id: "J", community_id: 3}),
(K:default {_id: "K", community_id: 3}),
(A)-[:default]->(B),
(A)-[:default]->(C),
(A)-[:default]->(D),
(A)-[:default]->(E),
(A)-[:default]->(G),
(D)-[:default]->(E),
(D)-[:default]->(F),
(E)-[:default]->(F),
(G)-[:default]->(D),
(G)-[:default]->(H),
(H)-[:default]->(K),
(I)-[:default]->(H),
(I)-[:default]->(J),
(J)-[:default]->(D),
(J)-[:default]->(K);
create().node_property(@default, "community_id", uint32);
insert().into(@default).nodes([{_id:"A", community_id: 1}, {_id:"B", community_id: 1}, {_id:"C", community_id: 1}, {_id:"D", community_id: 2}, {_id:"E", community_id: 2}, {_id:"F", community_id: 2}, {_id:"G", community_id: 1}, {_id:"H", community_id: 3}, {_id:"I", community_id: 3}, {_id:"J", community_id: 3}, {_id:"K", community_id: 3}]);
insert().into(@default).edges([{_from:"A", _to:"B"}, {_from:"A", _to:"C"}, {_from:"A", _to:"D"}, {_from:"A", _to:"E"}, {_from:"A", _to:"G"}, {_from:"D", _to:"E"}, {_from:"D", _to:"F"}, {_from:"E", _to:"F"}, {_from:"G", _to:"D"}, {_from:"G", _to:"H"}, {_from:"J", _to:"D"}, {_from:"I", _to:"H"}, {_from:"I", _to:"J"}, {_from:"H", _to:"K"}, {_from:"J", _to:"K"}]);
创建HDC图
将当前图集全部加载到HDC服务器hdc-server-1上,并命名为 my_hdc_graph:
CREATE HDC GRAPH my_hdc_graph ON "hdc-server-1" OPTIONS {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}
hdc.graph.create("my_hdc_graph", {
nodes: {"*": ["*"]},
edges: {"*": ["*"]},
direction: "undirected",
load_id: true,
update: "static"
}).to("hdc-server-1")
参数
算法名:conductance
参数名 |
类型 |
规范 |
默认值 |
可选 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
community_property |
"<@schema.?>property" |
/ | / | 否 | 代表社区ID的数值类型点属性 |
文件回写
CALL algo.conductance.write("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}, {
file: {
filename: "conductance"
}
})
algo(conductance).params({
projection: "my_hdc_graph",
community_property: "community_id"
}).write({
file: {
filename: "conductance"
}
})
community,conductance
2,0.4
1,0.4
3,0.2
完整返回
CALL algo.conductance.run("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(conductance).params({
community_property: "community_id"
}) as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
结果:
| community | conductance |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
流式返回
CALL algo.conductance.stream("my_hdc_graph", {
community_property: "community_id"
}) YIELD r
RETURN r
exec{
algo(conductance).params({
community_property: "community_id"
}).stream() as r
return r
} on my_hdc_graph
结果:
| community | conductance |
|---|---|
| 2 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
